配置工作原理
以下是一个 Dubbo 属性配置的例子 dubbo-spring-boot-samples
## application.properties
# Spring boot application
spring.application.name=dubbo-externalized-configuration-provider-sample
# Base packages to scan Dubbo Component: @com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.alibaba.boot.dubbo.demo.provider.service
# Dubbo Application
## The default value of dubbo.application.name is ${spring.application.name}
## dubbo.application.name=${spring.application.name}
# Dubbo Protocol
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=12345
## Dubbo Registry
dubbo.registry.address=N/A
## service default version
dubbo.provider.version=1.0.0
接下来,我们就围绕这个示例,分别从配置格式、配置来源、加载流程三个方面对 Dubbo 配置的工作原理进行分析。
1 配置格式
目前Dubbo支持的所有配置都是.properties格式的,包括-D、Externalized Configuration等,.properties中的所有配置项遵循一种path-based的配置格式。
在Spring应用中也可以将属性配置放到application.yml中,其树层次结构的方式可读性更好一些。
# 应用级配置(无id)
dubbo.{config-type}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 实例级配置(指定id或name)
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-id}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 服务接口配置
dubbo.service.{interface-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 方法配置
dubbo.service.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 方法argument配置
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{argument-index}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
1.1 应用级配置(无id)
应用级配置的格式为:配置类型单数前缀,无id/name。
# 应用级配置(无id)
dubbo.{config-type}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
类似 application、monitor、metrics 等都属于应用级别组件,因此仅允许配置单个实例;而 protocol、registry 等允许配置多个的组件,在仅需要进行单例配置时,可采用此节描述的格式。常见示例如下:
dubbo.application.name=demo-provider
dubbo.application.qos-enable=false
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=-1
1.2 实例级配置(指定id或name)
针对某个实例的属性配置需要指定id或者name,其前缀格式为:配置类型复数前缀 + id/name。适用于 protocol、registry 等支持多例配置的组件。
# 实例级配置(指定id或name)
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-id}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
- 如果不存在该id或者name的实例,则框架会基于这里列出来的属性创建配置组件实例。
- 如果已存在相同id或name的实例,则框架会将这里的列出的属性作为已有实例配置的补充,详细请参考属性覆盖。
- 具体的配置复数形式请参考单复数配置对照表
配置示例:
dubbo.registries.unit1.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.registries.unit2.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2182
dubbo.protocols.dubbo.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocols.dubbo.port=20880
dubbo.protocols.hessian.name=hessian
dubbo.protocols.hessian.port=8089
1.3 服务接口配置
dubbo.service.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.timeout=5000
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.timeout=6000
方法配置
方法配置格式:
# 方法配置
dubbo.service.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 方法argument配置
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{argument-index}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
方法配置示例:
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.timeout=7000
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.oninvoke=notifyService.onInvoke
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.onreturn=notifyService.onReturn
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.onthrow=notifyService.onThrow
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.0.callback=true
等价于XML配置:
<dubbo:reference interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService" >
<dubbo:method name="sayHello" timeout="7000" oninvoke="notifyService.onInvoke"
onreturn="notifyService.onReturn" onthrow="notifyService.onThrow">
<dubbo:argument index="0" callback="true" />
</dubbo:method>
</dubbo:reference>
1.4 参数配置
parameters参数为map对象,支持xxx.parameters=[{key:value},{key:value}]方式进行配置。
dubbo.application.parameters=[{item1:value1},{item2:value2}]
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.parameters=[{item3:value3}]
1.5 传输层配置
triple协议采用Http2做底层通信协议,允许使用者自定义Http2的6个settings参数
配置格式如下:
# 通知对端header压缩索引表的上限个数
dubbo.rpc.tri.header-table-size=4096
# 启用服务端推送功能
dubbo.rpc.tri.enable-push=false
# 通知对端允许的最大并发流数
dubbo.rpc.tri.max-concurrent-streams=2147483647
# 声明发送端的窗口大小
dubbo.rpc.tri.initial-window-size=1048576
# 设置帧的最大字节数
dubbo.rpc.tri.max-frame-size=32768
# 通知对端header未压缩的最大字节数
dubbo.rpc.tri.max-header-list-size=8192
等价于yml配置:
dubbo:
rpc:
tri:
header-table-size: 4096
enable-push: false
max-concurrent-streams: 2147483647
initial-window-size: 1048576
max-frame-size: 32768
max-header-list-size: 8192
1.6 属性与XML配置映射规则
可以将 xml 的 tag 名和属性名组合起来,用 ‘.’ 分隔。每行一个属性。
dubbo.application.name=foo相当于<dubbo:application name="foo" />dubbo.registry.address=10.20.153.10:9090相当于<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090" />
如果在 xml 配置中有超过一个的 tag,那么你可以使用 ‘id’ 进行区分。如果你不指定id,它将作用于所有 tag。
dubbo.protocols.rmi.port=1099相当于<dubbo:protocol id="rmi" name="rmi" port="1099" />dubbo.registries.china.address=10.20.153.10:9090相当于<dubbo:registry id="china" address="10.20.153.10:9090" />
1.7 配置项单复数对照表
复数配置的命名与普通单词变复数的规则相同:
- 字母y结尾时,去掉y,改为ies
- 字母s结尾时,加es
- 其它加s
| Config Type | 单数配置 | 复数配置 |
|---|---|---|
| application | dubbo.application.xxx=xxx | dubbo.applications.{id}.xxx=xxx dubbo.applications.{name}.xxx=xxx |
| protocol | dubbo.protocol.xxx=xxx | dubbo.protocols.{id}.xxx=xxx dubbo.protocols.{name}.xxx=xxx |
| module | dubbo.module.xxx=xxx | dubbo.modules.{id}.xxx=xxx dubbo.modules.{name}.xxx=xxx |
| registry | dubbo.registry.xxx=xxx | dubbo.registries.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| monitor | dubbo.monitor.xxx=xxx | dubbo.monitors.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| config-center | dubbo.config-center.xxx=xxx | dubbo.config-centers.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| metadata-report | dubbo.metadata-report.xxx=xxx | dubbo.metadata-reports.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| ssl | dubbo.ssl.xxx=xxx | dubbo.ssls.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| metrics | dubbo.metrics.xxx=xxx | dubbo.metricses.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| provider | dubbo.provider.xxx=xxx | dubbo.providers.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| consumer | dubbo.consumer.xxx=xxx | dubbo.consumers.{id}.xxx=xxx |
| service | dubbo.service.{interfaceName}.xxx=xxx | 无 |
| reference | dubbo.reference.{interfaceName}.xxx=xxx | 无 |
| method | dubbo.service.{interfaceName}.{methodName}.xxx=xxx dubbo.reference.{interfaceName}.{methodName}.xxx=xxx | 无 |
| argument | dubbo.service.{interfaceName}.{methodName}.{arg-index}.xxx=xxx | 无 |
2 配置来源
Dubbo 默认支持 6 种配置来源:
- JVM System Properties,JVM -D 参数
- System environment,JVM进程的环境变量
- Externalized Configuration,外部化配置,从配置中心读取
- Application Configuration,应用的属性配置,从Spring应用的Environment中提取"dubbo"打头的属性集
- API / XML /注解等编程接口采集的配置可以被理解成配置来源的一种,是直接面向用户编程的配置采集方式
- 从classpath读取配置文件 dubbo.properties
关于dubbo.properties属性:
- 如果在 classpath 下有超过一个 dubbo.properties 文件,比如,两个 jar 包都各自包含了 dubbo.properties,dubbo 将随机选择一个加载,并且打印错误日志。
- Dubbo 可以自动加载 classpath 根目录下的 dubbo.properties,但是你同样可以使用 JVM 参数来指定路径:
-Ddubbo.properties.file=xxx.properties。
2.1 覆盖关系
如果通过多种配置来源指定了相同的配置项,则会出现配置项的互相覆盖,具体覆盖关系和优先级请参考下一小节。
3 配置加载流程
3.1 处理流程
Dubbo 配置加载大概分为两个阶段:
- 第一阶段为DubboBootstrap初始化之前,在Spring context启动时解析处理XML配置/注解配置/Java-config 或者是执行API配置代码,创建config bean并且加入到ConfigManager中。
- 第二阶段为DubboBootstrap初始化过程,从配置中心读取外部配置,依次处理实例级属性配置和应用级属性配置,最后刷新所有配置实例的属性,也就是属性覆盖。
3.2 属性覆盖
发生属性覆盖可能有两种情况,并且二者可能是会同时发生的:
- 不同配置源配置了相同的配置项
- 相同配置源,但在不同层次指定了相同的配置项
3.2.1 不同配置源
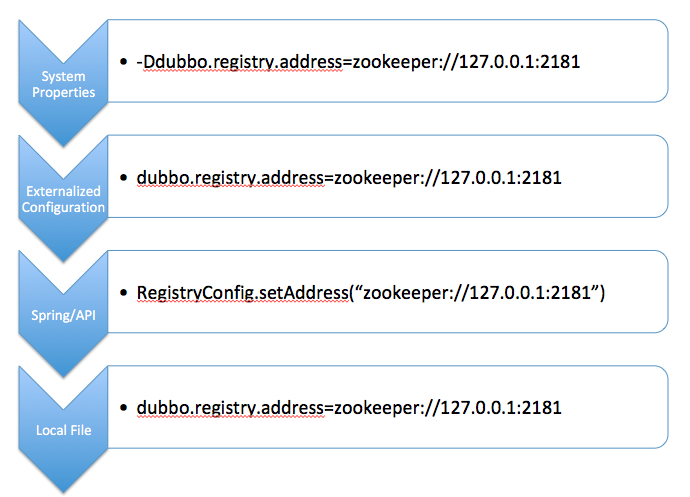
3.2.1 相同配置源
属性覆盖是指用配置的属性值覆盖config bean实例的属性,类似Spring PropertyOverrideConfigurer 的作用。
Property resource configurer that overrides bean property values in an application context definition. It pushes values from a properties file into bean definitions. Configuration lines are expected to be of the following form:
beanName.property=value
但与PropertyOverrideConfigurer的不同之处是,Dubbo的属性覆盖有多个匹配格式,优先级从高到低依次是:
#1. 指定id的实例级配置
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-id}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
#2. 指定name的实例级配置
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
#3. 应用级配置(单数配置)
dubbo.{config-type}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
属性覆盖处理流程:
按照优先级从高到低依次查找,如果找到此前缀开头的属性,则选定使用这个前缀提取属性,忽略后面的配置。
3.3 外部化配置
外部化配置目的之一是实现配置的集中式管理,这部分业界已经有很多成熟的专业配置系统如 Apollo, Nacos 等,Dubbo 所做的主要是保证能配合这些系统正常工作。
外部化配置和其他本地配置在内容和格式上并无区别,可以简单理解为 dubbo.properties 的外部化存储,配置中心更适合将一些公共配置如注册中心、元数据中心配置等抽取以便做集中管理。
# 将注册中心地址、元数据中心地址等配置集中管理,可以做到统一环境、减少开发侧感知。
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.registry.simplified=true
dubbo.metadata-report.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
dubbo.application.qos.port=33333
优先级 外部化配置默认较本地配置有更高的优先级,因此这里配置的内容会覆盖本地配置值,关于各配置形式间的覆盖关系 有单独一章说明。
作用域 外部化配置有全局和应用两个级别,全局配置是所有应用共享的,应用级配置是由每个应用自己维护且只对自身可见的。当前已支持的扩展实现有 Zookeeper、Apollo、Nacos。
3.3.1 外部化配置使用方式
- 增加 config-center 配置
<dubbo:config-center address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
- 在相应的配置中心(zookeeper、Nacos 等)增加全局配置项,如下以 Nacos 为例:
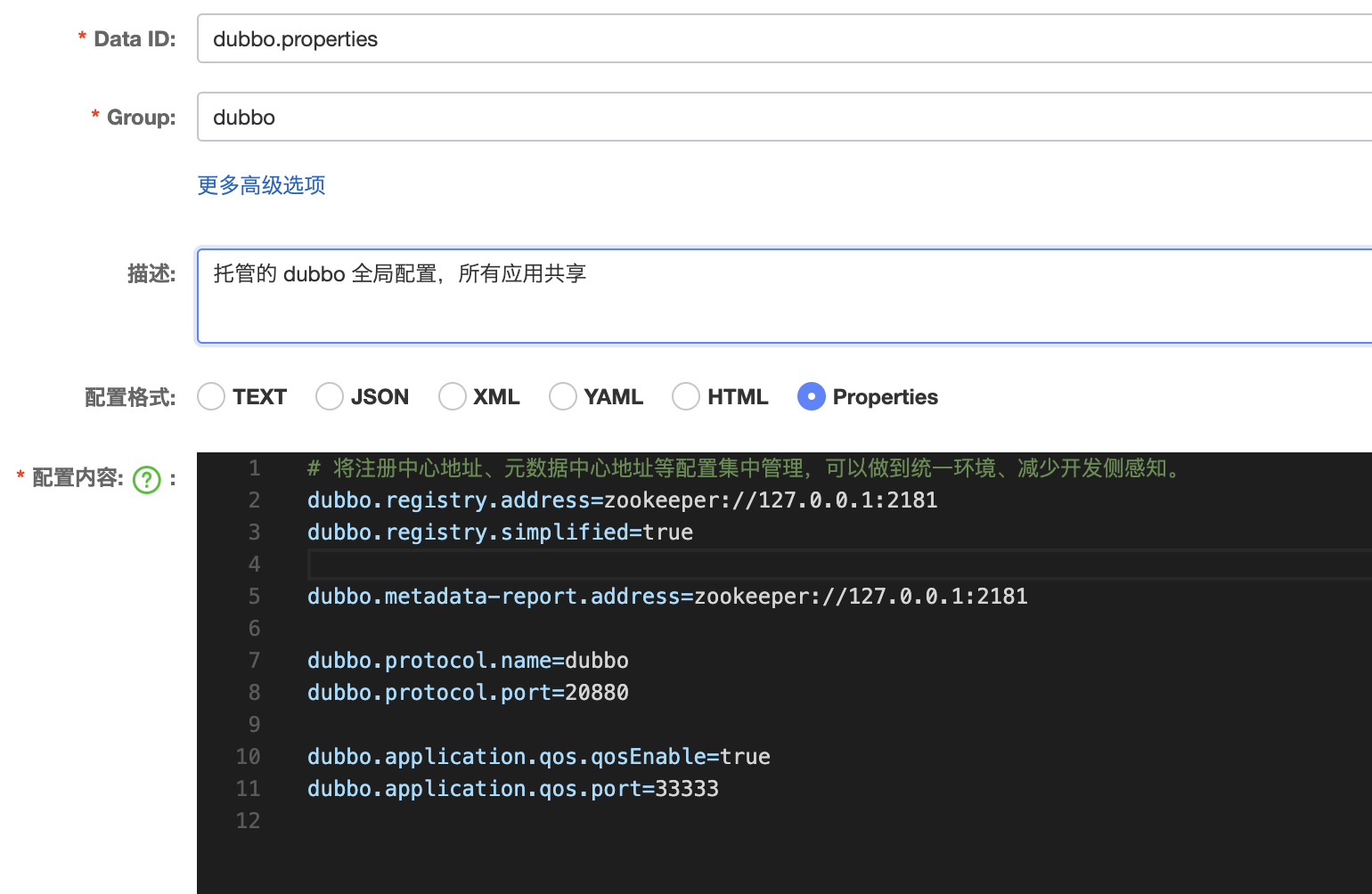
开启外部化配置后,registry、metadata-report、protocol、qos 等全局范围的配置理论上都不再需要在应用中配置,应用开发侧专注业务服务配置,一些全局共享的全局配置转而由运维人员统一配置在远端配置中心。
这样能做到的效果就是,应用只需要关心:
- 服务暴露、订阅配置
- 配置中心地址 当部署到不同的环境时,其他配置就能自动的被从对应的配置中心读取到。
举例来说,每个应用中 Dubbo 相关的配置只有以下内容可能就足够了,其余的都托管给相应环境下的配置中心:
dubbo
application
name: demo
config-center
address: nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
3.3.2 自行加载外部化配置
所谓 Dubbo 对配置中心的支持,本质上就是把 .properties 从远程拉取到本地,然后和本地的配置做一次融合。理论上只要 Dubbo 框架能拿到需要的配置就可以正常的启动,它并不关心这些配置是自己加载到的还是应用直接塞给它的,所以Dubbo还提供了以下API,让用户将自己组织好的配置塞给 Dubbo 框架(配置加载的过程是用户要完成的),这样 Dubbo 框架就不再直接和 Apollo 或 Zookeeper 做读取配置交互。
// 应用自行加载配置
Map<String, String> dubboConfigurations = new HashMap<>();
dubboConfigurations.put("dubbo.registry.address", "zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");
dubboConfigurations.put("dubbo.registry.simplified", "true");
//将组织好的配置塞给Dubbo框架
ConfigCenterConfig configCenter = new ConfigCenterConfig();
configCenter.setExternalConfig(dubboConfigurations);
